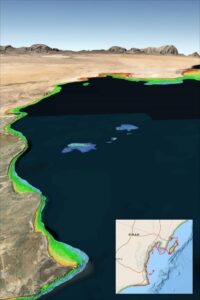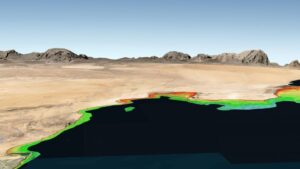
One of many challenges when entering a new harbor is not knowing accurate depths. Recent occurrences of groundings off the coasts of Oman, Greenland and Fiji were under investigation in early October and the underlying causes were complicated.
One common thread is a lack of current bathymetric data in coastal areas, particularly those outside established shipping lanes.
Denver-based TCarta Marine uses earth observation satellites to provide accurate water depth measurements for near-shore areas. “The risk of such accidents can be significantly reduced with up-to-date bathymetric data produced from satellite imagery,” TCarta president Kyle Goodrich said in a statement. In many coastal regions, the waters beyond commercial shipping lanes are poorly charted, or in some cases, not surveyed at all.
Traditionally, gathering high-quality depth measurements in remote coastal areas has been expensive and hazardous because it involves using mapping aircraft and vessels. “The risk of groundings is only growing as military vessels and eco-tourism charters increasingly operate in unfamiliar and inadequately mapped coastal zones,” said Goodrich.
For more than a decade, TCarta has been supplying marine charting organizations with water depth data through a technique called satellite derived bathymetry. This relies on physics-based algorithms applied to optical imagery captured by commercial satellites. By detecting and measuring the light that reflects off the seafloor, SDB calculates water depths, reaching depths of 66 to 98 feet depending on water clarity.
Goodrich says that SDB is safer than other forms of depth acquisition because it poses no danger to personnel, equipment or coastal environments. Plus, satellites can operate without geographic constraints, allowing data collection in areas that could be inaccessible to vessels or aircraft.
TCarta has mapped nearly a third of the world’s coastlines using SDB. The firm offers ready-made and custom bathymetric offerings. Custom datasets leverage high-resolution satellite imagery to achieve a one-meter resolution with feature details including shoals and reefs. The off-the-shelf, global satellite derived provides detail up to 33 feet and can detect coastal shoals in remote areas. The product is readily available for locations including the South China Sea, Arabian/Persian Gulf, Gulf of Oman, the Red Sea, the Black Sea and the eastern Mediterranean.